Anatomy – The study of the structure of the body and the relationships between the structures.
Physiology – Study of the function of the body parts
Pathology – Structural and functional changes associated with diseases.
- Etiology – Etio =cause. Study of the cause of disease
- Sign – Objective evidence of disease that can be observed or measured.
- Symptom – Subjective change in body function not apparent to an observer and can’t be measured.
- Treatment – the management and care of a patient or client
Levels of Structural Organization
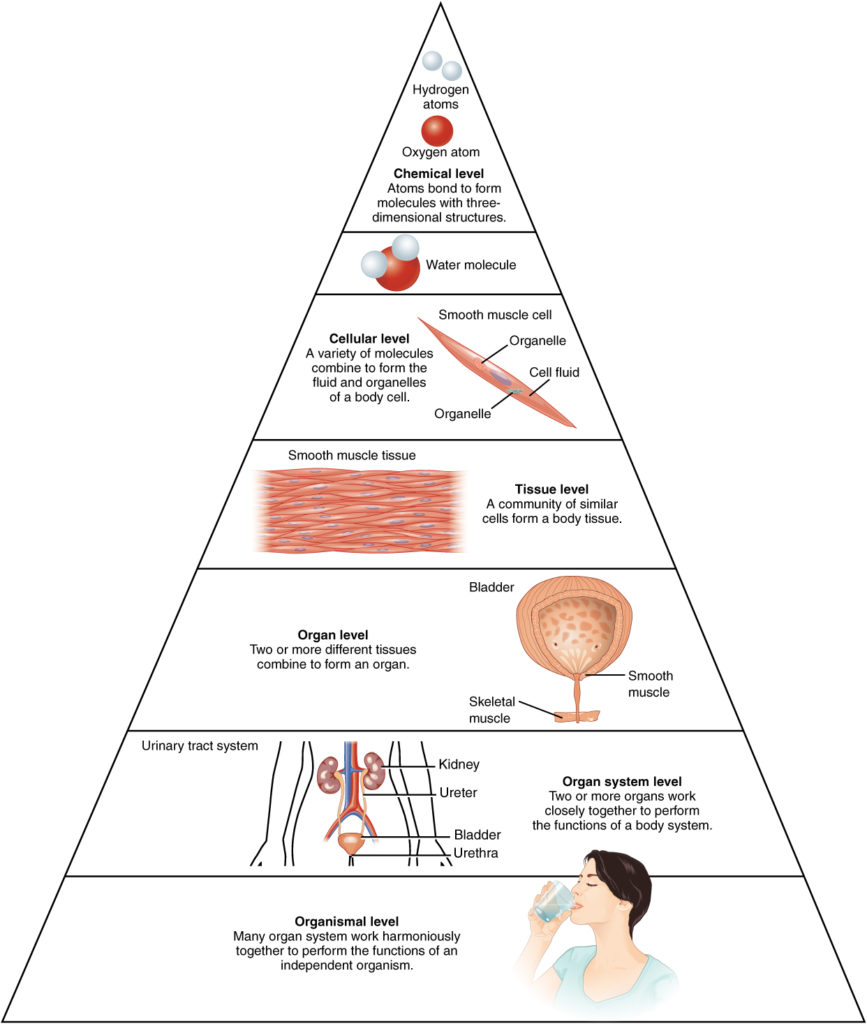
- Atoms – Smallest building block of matter made up of protons, electrons and neutrons. Two or more atoms combine to form molecules which are the building block of body structures. Some examples are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
- Chemicals – Subatominc particles, atoms and molecules form elements which essential for maintaining life
- Cellular – basic structural and functional units are called cells of an organism (muscle cells, nerve cells, blood cells)
- Tissues – A group of similar cells that have a similar origin in the embryo and perform specific functions. The four basic tissue types are epithelium, connective tissue, muscle tissue, nerve tissue.
- Organs – Composed of two or more different tissues and have specific functions and recognizable shape. Examples: brain, stomach, liver.
- System – Related organs that have a common function like the digestive system that is composed of the mouth, salivary glands, throat, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, gall bladder and pancreas. The systems are integumentary, skeletal, nervous, muscular, endocrine, respiratory, lymphatic, digestive, urinary and reproductive systems.
- Organism – Living individual
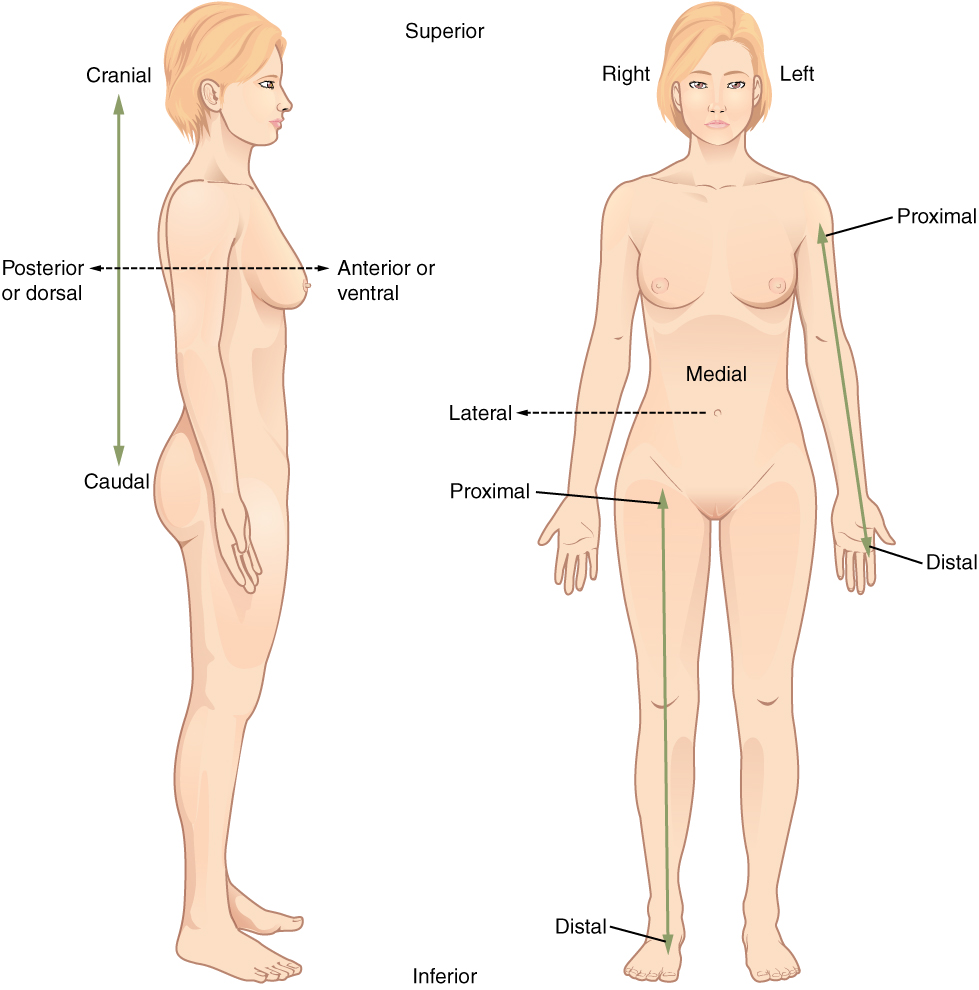
Anatomical Position – erect, palms forward, feet flat on the floor, arms at the side.
- Prone – lying horizontal, face down
- Supine- lying horizontal, face up
- Superior- above or in a higher position
- Inferior- below or lower position
- Anterior – ventral – front
- Posterior – dorsal – back
- Cranial – near the head
- Caudal – near the sacral region of spinal column
- Medial – toward midline of the body
- Lateral – away from the midline towards the side
- Contralateral –
- ipsilateral
- Proximal – nearest the origin of a structure
- Distal – farthest away from a region
- Superficial – towards surface
- Deep – Internal
- Palmar
- Dorsal
- Ventral
- Plantar
- Peripheral
- Central
- Internal
- External
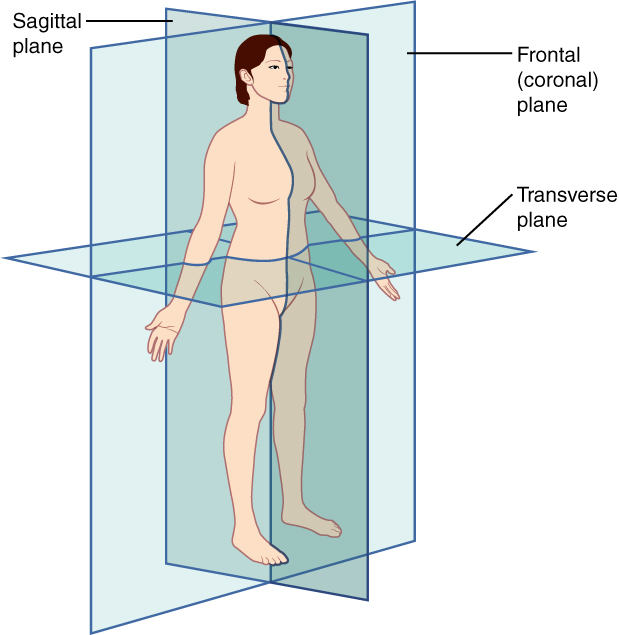
Planes of the body
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/1-introduction
- Midsagittal – Vertical Plane that divides the body or organ into right and left sides. A Midsaggital plane passes through the midline.
- Frontal – (coronal) divides the body or organ into anterior and posterior (front and back)
- Horizontal or Transverse – divides the body or organ into superior and inferior
- Oblique – divides the body or organ at an angle
Body movements
- flexion
- extension
- Abduction
- adduction
- rotation
- medial rotation
- lateral rotation
- left or right lateral flexion
- supination
- pronation
- elevation
- depression
- protraction
- retraction
- upward rotation
- downward rotation
- inversion
- eversion
- dorsiflexion
- plantar flexion
- circumduction
Body Regions
Head (Cephalic)
- Skull (Cranial)
forehead (frontal) - Face – Facial
eye – Orbital
ear – Otic
cheek – Buccal
nose – Nasal
mouth – Oral
chine- Mental - Neck – Cervical
- Shoulder- Acromial
- Upper Extremity
armpit – axillary
arm- brachial
Front of elbow- antecubital
Back of elbow- Olecranial
Wrist- carpal
Palm – metacarpal
Posterior surface of hand – dorsal
Fingers – Phalangeal - Trunk –Front
Chest – thoracic
Breast- mammary - Abdomen
Navel – umbilical
Hip – Coxal
Pelvis
Pubis- Pubic - Trunk –the Back
Back – Dorsal
Loin – Lumbar - Lower Extremity
Buttock – Gluteal
Thigh- Femoral
Anterior knee – Popliteal
Leg – Crural
Calf – Sural - Foot – Pedal
Ankle – Tarsal
Top of Foot – Dorsal
Sole of Foot- Plantar
Heel- Calcaneal
Toes – Digital or Phalangeal
Body Cavities
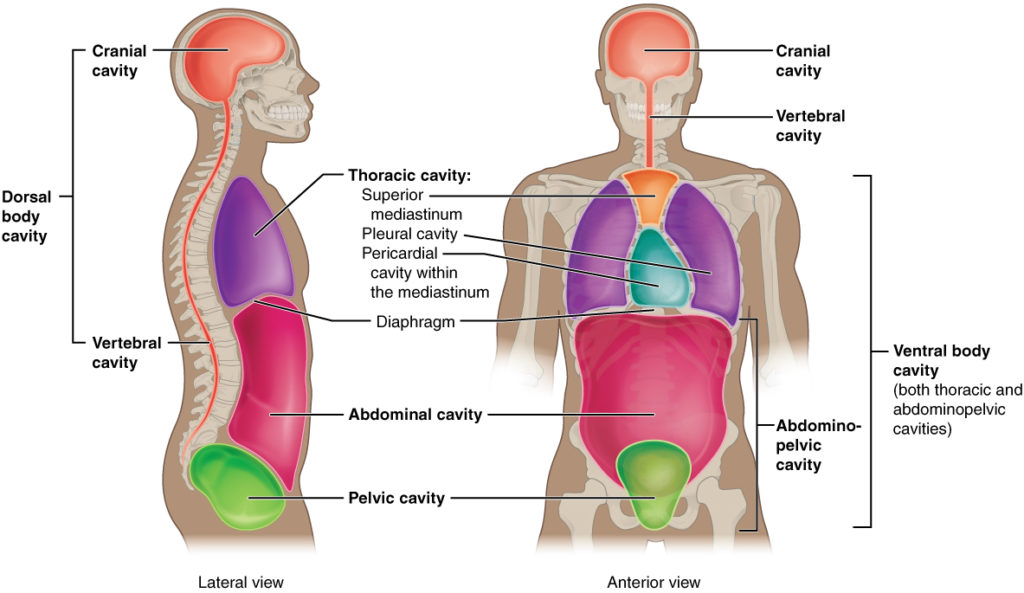
- Dorsal Cavity – Posterior
Cranial Cavity – skull (cranial ) bones, contain the brain
Spinal Cavity – or vertebral cavity; vertebrae which contains the spinal cord - Ventral Cavity – Anterior; two subdivisions
Thoracic Cavity – chest cavity, enclosed by ribs; separated from the abdominal cavity by the diaphragm. contain heart and lungs.
Made up of Pleural cavity which contains the lungs. Pericardial cavity contains the heart. Mediastinum contains the lungs from the breastbone to the vertebrae that contain the heart, thymus, esophagus, trachea and several blood vessels and lymphatic vessels
Abdominopelvic cavity – area below diaphragm;
Abdominal Cavity – contains stomach, spleen, liver, pancreas, small intestine and most of large intestine
Pelvic Cavity – contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs and some large intestines. - Abdominal quadrants:
right upper quadrant – (RUQ) stomach, duodenum, liver, gall bladder, rt. transverse colon
left upper quadrant – (LUQ ) stomach, spleen, left transverse colon
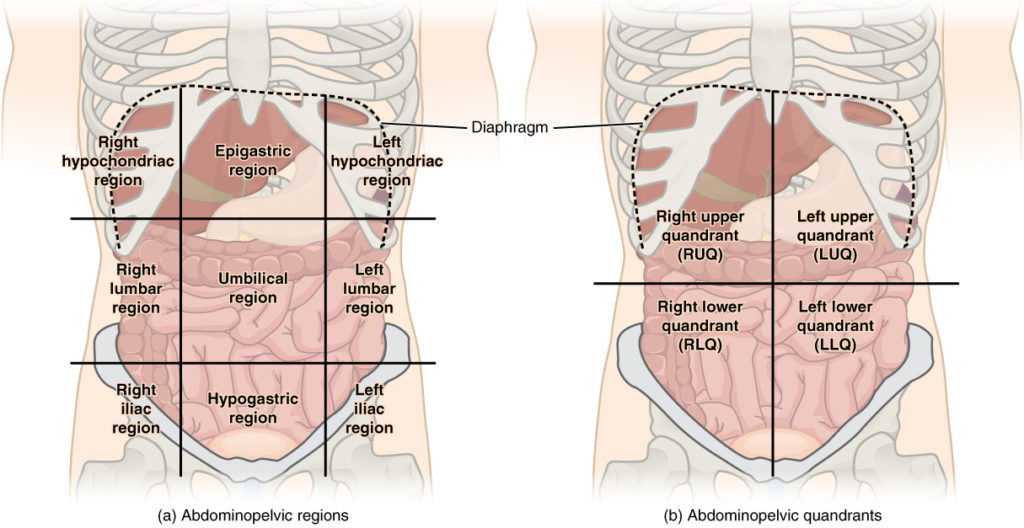
right lower quadrant – (RLQ) appendix, ascending colon, sacroiliac joint
left lower quadrant – ( LLQ) descending colon, sacroiliac joint